Accounting for leases in accordance with IFRS 16 can be a complex task for companies that handle many leases with constant changes. In this article, you can read more about how IFRS 16 differs from previous accounting standards and what challenges and changes it entails for businesses. Furthermore, we want to show how an IFRS 16 software can help you with handling.
How to choose IFRS 16 software
Accounting for leases according to IFRS 16 can be a complicated task, especially if you handle this in Excel. In this article, we want to show why all businesses with more than lease agreements should purchase an IFRS 16 software equivalent to ShareControl IFRS 16.
What is IFRS 16?
IFRS 16 is the new standard for accounting for leases that was published in January 2016. The goal of this standard is to make lease accounting more transparent and comparable across organizations. The new standard replaces IAS 17, which was released in 1993.
Under IFRS 16, lessees will be required to recognize most leases on their balance sheet. This can be a complex process, something an IFRS 16 software can help with. These are systems that have been specially developed to help businesses with the IFRS 16 provisions, throughout the entire process from identification to balance sheet entry.
Find out more about IFRS 16: What is IFRS 16?

What has changed under IFRS 16?
The main difference between IFRS 16 and IAS 17 is that lessees will now be required to recognize most leases on their balance sheet. This means that businesses must provide more information about their leasing agreements than under the old standard for accounting for lease agreements.
Businesses must now provide more information about their leases, including the total amount of lease payments, the lease term and the interest rate.
Good control of the lease agreements is therefore essential for handling the company’s accounts in accordance with IFRS 16. With the ShareControl IFRS 16 software, you can safely and efficiently manage all aspects of your leasing agreements, and ensure that your company meets the standard’s requirements in a flexible and reliable way.
What is considered a lease under IFRS 16?
IFRS 16 defines a lease as an agreement that gives a lessee the right to use an identifiable asset (such as a building, machine, vehicle or other type of asset) for an agreed period of time against payment to the lessor. This agreement can be written, oral or implied, as long as it gives the lessee rights to use the asset. A lease can therefore be defined as an agreement between two parties, lessor and lessee, where the lessor agrees to give the lessee the right to use an asset for a specified period of time.
For an agreement to qualify as a lease according to IFRS 16, it must meet the following criteria:
- Identifiable asset: The agreement must identify a specific asset that the lessee has the right to use. This can be a physical asset, such as a car or office space, or an intangible asset, such as a license to use software.
- Right to use: The lessee must have the right to use the identified asset for the specified time period. This means that the tenant has control over how and when the asset is used, even if the landlord still owns it.
- Exclusive right to use: The lessee must have the exclusive right to use the asset for the specified time period. This means that the lessor cannot give other parties rights to use the same asset in the same period.
- Lease term of at least 12 months: The lease must have an agreed lease term of at least 12 months or more, unless the asset is of low value (under $5,000) or the lease contains options to extend the lease term.
Typical lease agreements according to IFRS 16:
- Lease of buildings and premises: This may include the lease of office premises, retail premises, factories, warehouses and other commercial property. Such leases can be of varying length and can include various extras such as common areas, parking spaces and security services.
- Lease of equipment and machinery: This includes lease agreements for equipment and machinery that are necessary for the company’s operation, for example production equipment, IT equipment, vehicles and other specialized equipment. Leases for equipment can be more flexible than leases for real estate and can vary in duration and scope.
- Leasing of means of transport: This includes lease agreements for means of transport such as cars, trucks, buses, planes and ships. Such leases can be crucial for companies involved in transport and logistics, and can have different terms depending on the needs of the tenant.
- Leasing of IT services and software: This includes leases for IT services, software licenses and other technological infrastructure necessary for the operation of the business, such as cloud-based services, software subscriptions and data centres.
- Operating leasing of financial assets: Under IFRS 16, certain leases that were previously classified as operating leases may now be classified as financial assets and liabilities due to the standard’s new rules. This includes leases where the lessee gains control of the asset for substantially the entire lease term or where the lease contains a purchase option at a price expected to give the lessor a significant portion of the asset’s fair value.
What challenges are there?
IFRS 16 can be a complex standard to comply with, particularly for lessees. This is because most leases will now need to be recognized on the balance sheet. Some of the challenges associated with IFRS 16 include:
- The complexity of calculation and administration: Calculation of lease obligations under IFRS 16 can be complicated, especially for companies with many and complex lease agreements. The administration of these agreements requires careful follow-up and accuracy.
- The need for accurate information and data management: IFRS 16 requires accurate information about lease agreements, including lease payments, lease periods, and valuation of assets and liabilities. This requires thorough data management and quality assurance to ensure that the information reported is correct.
- Changes in business practices and controls: The implementation of IFRS 16 may require changes in the company’s business practices and control processes to ensure that all leases are properly identified, assessed and reported in accordance with the standard.
- Impact on key figures and analyses: The changes introduced by IFRS 16 may affect key figures and financial analyses, which may have consequences for the company’s performance and decision-making processes. It is important to understand these effects and adapt analysis methods and tools accordingly.
How does IFRS 16 affect financial reporting?
IFRS 16 will have a significant impact on financial reporting. This includes:
Change in accounting for leases: Previously, leases were treated as operating leases, and lease payments were only reported as operating costs in the profit and loss account. With the introduction of IFRS 16, most leases must now be recognized as assets and liabilities on the balance sheet. This will have a significant impact on the company’s balance sheet and financial position.
Impact on key figures and financial analyses: The change in how lease agreements are treated in the accounts will also affect important financial key figures and analyses. For example, the debt ratio and equity ratio will change as a result of including lease liabilities on the balance sheet. It is important to understand these changes in order to correctly interpret and analyze the company’s financial situation.
Increased complexity in accounting: The implementation of IFRS 16 can lead to increased complexity in accounting, especially for companies with many and complex lease agreements. It requires thorough assessment of leases, calculation of lease liabilities and careful documentation to ensure accurate reporting in accordance with the standard.
Need for training and competence: The changes introduced by IFRS 16 may also require training and competence enhancement among accountants and finance personnel to ensure correct implementation and compliance with the standard. This includes an understanding of the new accounting principles, calculation methods and reporting requirements under IFRS 16.
What are the benefits?
Despite the challenges with IFRS 16, there are several key advantages. One of the main advantages is that the IFRS 16 standard helps to increase transparency in the companies’ accounting reporting by requiring that all significant leases be entered in the balance sheet. This gives investors and other stakeholders better insight into the company’s financial situation and lease obligations.
By including lease agreements on the balance sheet, the company’s financial position is more accurately reflected. This can help the businesses to make better decisions related to investments or credit from investors, the board and other stakeholders.
Through the classification of lease agreements, businesses will gain greater flexibility and control over how they treat their lease obligations. This can contribute to better strategic planning and management of the company’s rental portfolio.
Furthermore, IFRS 16 will help to reduce the complexity of financial reporting by establishing clear guidelines for how lease agreements are to be treated. This also promotes consistency in accounting practices across different organizations and industries, which makes it easier to compare rental accounts between companies.
ShareControl IFRS16
ShareControl IFRS 16 has been developed with all the necessary functions to ensure full compliance with the IFRS 16 standard. With a comprehensive package covering everything from lease contract registration to automatic calculation of lease payments and reporting tools to prepare accounts in accordance with IFRS 16, ShareControl is a comprehensive solution for managing leases efficiently.
ShareControl IFRS 16 is built on Microsoft 365, which ensures a user-friendly, secure and efficient system for IFRS 16 handling.
One of the unique advantages of ShareControl IFRS 16 is that it is delivered as a Microsoft 365 add-in for SharePoint. This means that it integrates seamlessly with existing SharePoint environments, giving users a user-friendly and familiar platform to work with. In addition, Microsoft 365 offers a high level of security, with advanced features such as data security, compliance with privacy laws and protection against cyber threats. This gives users peace of mind and confidence that their sensitive rental data is protected against unauthorized access and loss.
ShareControl IFRS 16 software can help you with all aspects of complying with the IFRS 16 standard. The system is delivered as a Microsoft 365 add-in that ensures quick installation and a user-friendly process.
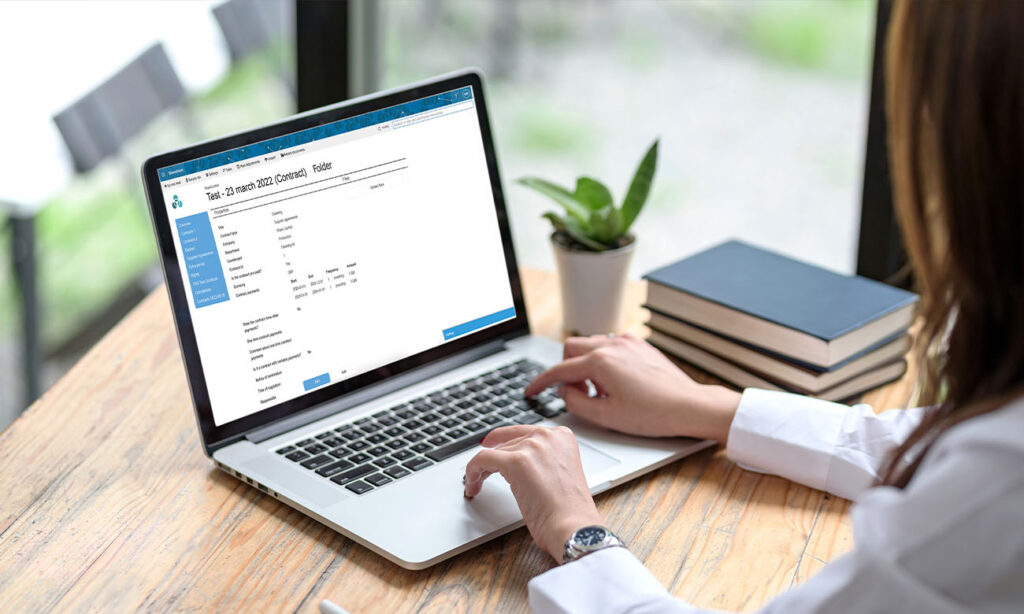
Some of the benefits of ShareControl IFRS 16 are:
- A lease register that records all leases in one place
- The ability to track changes to leasing agreements
- Automatic calculation of lease payments
- Reporting tools that help you prepare financial statements in accordance with IFRS 16
If you are looking for software to help you comply with IFRS 16, ShareControl is a good option. It is easy to use and includes everything you need to manage your leasing agreements effectively.
Read also: Implementation of IFRS 16 before listing









